Family, culture, and community provide the essential foundation for a child’s development both mentally, physically and socially. In order to have children succeed in society, educators need to help children by learning about their complex environments and different interactions they have in their daily lives. By learning more about their children, educators can better understand who they are as individuals, how they relate to others and what they aspire to be as adults.
Family
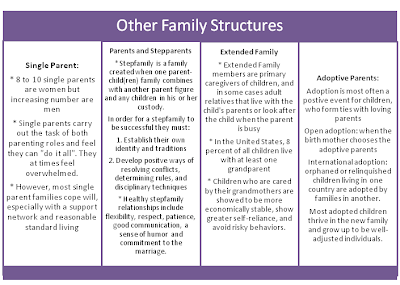
A family is defined as having two or more people who live together and are related by such enduring factors as birth, marriage, adoption, or long-term mutual commitment. Families come in a variety of different forms such as: two-parent families, single-parent families, stepfamilies, adoptive families, foster families, extended families and much more. Nonetheless, family members are key figures in the socialization of children by encouraging certain beliefs and behaviors onto their children.
Family Structure
Family Structure refers the children in a family home and the adults who live with and care for the children. Based on the Federal Interagency Forum on Child and Family Statistics (2007), 67 percent of American children live with two parents, 23 parents live with their mother only, 5 percent live with their father only and 5 percent live without a parent in their household and reside with other family members. Families come in a variety of ways and this blog will discuss a few and how they benefit or hinder a child’s development.
When mothers and fathers are both present in the home children tend to form close bonds with both parents. Being nurtured by two parents provides advantageous for children because they have two loving role models and magnifies the affection they receive.
Divorcing Parents: In the United States, one and five first marriages end in divorce or separation within five years of the wedding. Even though these numbers are high, children who deal with divorcing parents are heartbroken, overwhelmed and confused. In order to help children cope during the divorce process, some strategies parents should consider are:
Effective coping skills allow children to accept the divorce and not blame themselves and remain hopefully and optimistic about the future.
Family Processes
Family Processes are the interchanges that children have with family members. One of these factors that affect and influence children is parenting styles which are:
Accommodating Diverse Family Structure:
Family support and involvement is important to the success of a child. In order for familes to feel appreciated and valued. Educators shoud use specific tactics such as:
Culture
Culture refers to the characteristic behaviors and beliefs of a long-standing social group. Culture behaviors include the everyday routines that families and children carry out as they maintain households, work, and play, use tools and relate to one another. Cultural behaviors also include a group’s periodic rituals, such as worshipping and celebrating holidays. Individualistic cultures are cultural group that encourage independence, self-assertion, competition, and expression of personal needs. Collectivistic culture are cultural group that encourage obedience to and dependence on authority figures and being honorable, cooperative, and invested in group accomplishments. Growing up in a culture, children experience human life as being predictable and meaningful. Culture also adds an intellectual dimension to life by exposing children to the wisdom, discoveries and creative aspects of society.
Children's Experiences in Diverse Groups
Ethnicity has a powerful influence on children and their families because a child’s ethnicity indicates his or her affiliation with a group of individuals who share certain values, beliefs, behaviors, and often common cultural history and heritage. A ethnic group may be comprised of people of the same race, national origins, or religious background. Cultural and ethnic differences become salient when people move from one environment to another. When different cultural groups exist in the same region, the two groups interact and learn about one another. As people participate in the customs and take on the values of a new culture, acculturation occurs. Acculturation has four different forms:
Community
Community is the neighborhood in which a child and his family live and the surrounding vicinity. Community provides a bridge for families to the outside world by supplying playmates and outlets for children’s recreation. Communities also provide children and parents with social networking and services such as friends who can supervise children’s activities, model and offer advice on effective parenting strategies, and provide the emotional support that parents need, in times of need. Furthermore, communities tells children what society wants them to be as adults and a community can provide positive role models when a child does not have one at home.
Family Income/PovertyA child’s experience in a community is strongly affected by family’s personal and financial resources. Socioeconomic status is one’s general stranding in an economically stratified society, encompassing family income, type of job and educational level. About 17 percent of United States children live in poverty. Children and adolescents living in poverty face serious challenges such as poor nutrition and health care, inadequate housing and material good, toxic environments, gaps in background knowledge, increased probability of disabling conditions, emotional stress, lower quality schools and public misconceptions.
How to make a difference
Making schools family friendly